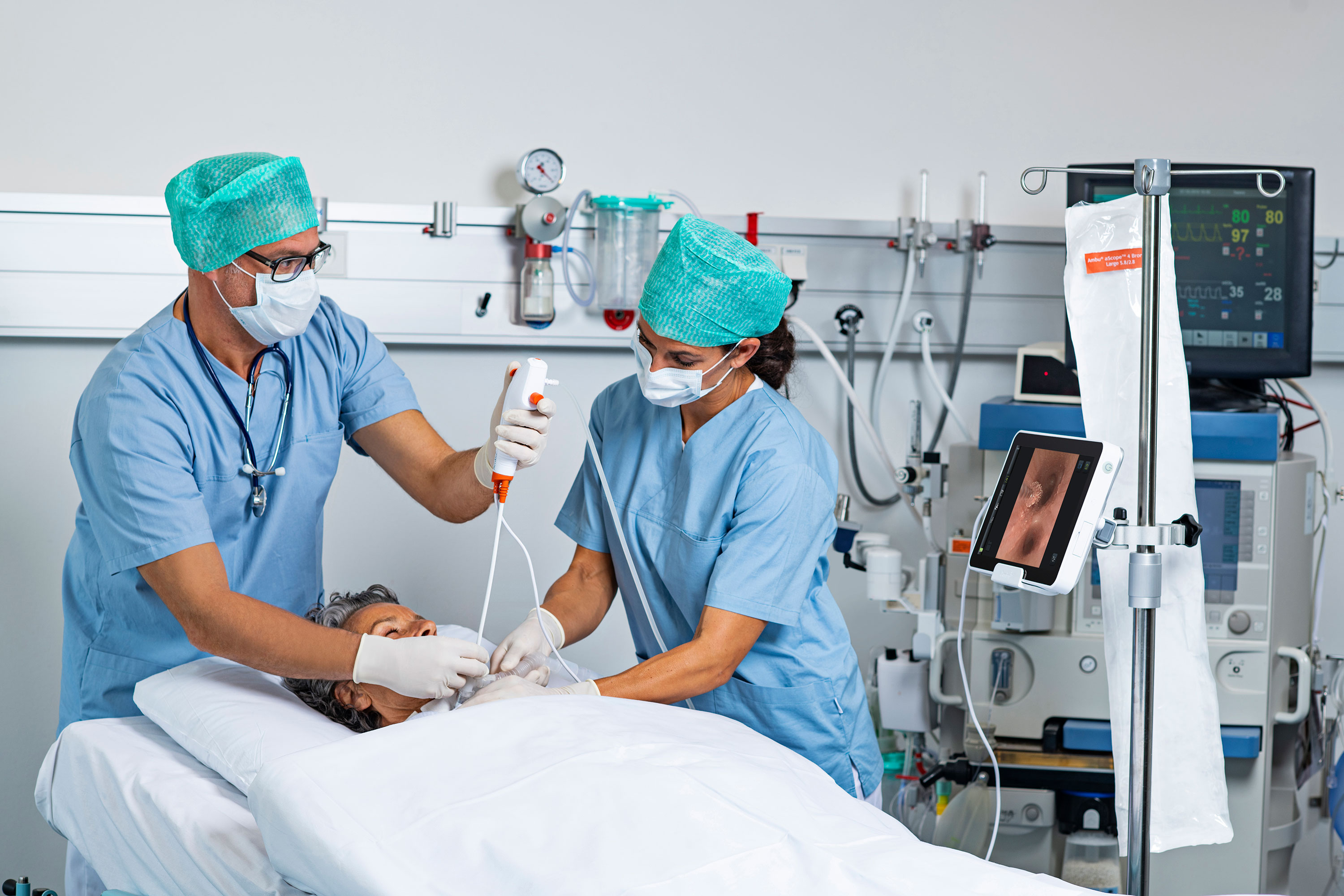
Many advances have been made in detecting and treating bladder cancer in recent years, but cystoscopy remains the gold standard in diagnosing the disease.
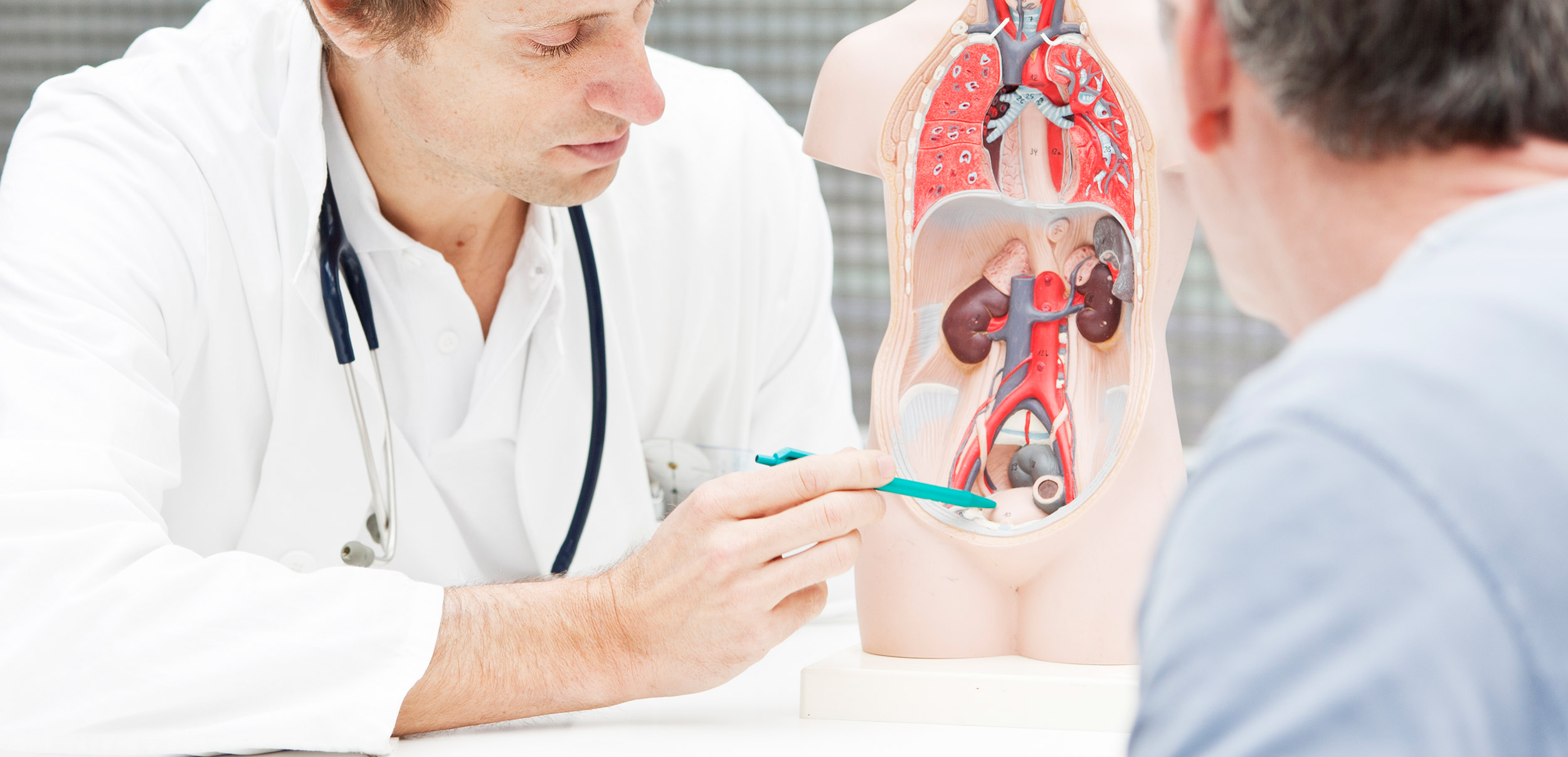
This is according to Dr. Yair Lotan, professor of urology and chief of urologic oncology at UT Southwestern Medical Center. He recently discussed alternatives to cystoscopy for bladder cancer diagnosis and why each must be used along with, instead of in place of, cystoscopy on the Bladder Cancer Matters podcast.
Lotan said cystoscopy should be the main tool to examine a patient with blood in the urine, the most common sign of bladder cancer. The evaluation usually includes imaging — either a CT scan or an ultrasound.
Large tumors or growths can be seen through imaging, but many bladder cancer tumors are smaller. And if the bladder is collapsed, imaging cannot detect solid areas within the bladder, Lotan explained.
“Unfortunately, imaging is not very useful in looking for tumors in hollow organs, and that is why people have to do colonoscopy to evaluate the lining of the colon and why we have to do cystoscopy to evaluate the lining of the bladder,” he said.
Alternatives to Cystoscopy
Tools to detect bladder cancer through blood samples have not been validated and are not yet commercially recommended.
Urine markers, however, recently received FDA approval. These take a close look at biomarkers such as DNA, RNA, or proteins.
“The problem with some of these markers is that they can also miss some high-grade cancers and they also have the potential for false positive results,” Lotan said. “They are being used in various different clinical scenarios, but not yet to replace cystoscopy.”
Then there's cytology, the process of examining urine for any suspicious cells. It has a low sensitivity to low-grade cancers, Lotan said, and can miss between 30 percent and 50 percent of high-grade cancers.
Because cystoscopy relies on the urologist to spot cancerous tumors, which can be difficult to detect when small or flat, cytology serves “as an adjunct measure to try to catch any cancers that were missed,” he added.